How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both beginners and experienced pilots. This guide provides a step-by-step approach, covering everything from understanding basic drone components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight techniques and adhering to safety regulations. We’ll explore the intricacies of drone control, camera operation, and troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re well-equipped to navigate the exciting world of aerial flight.
From understanding the fundamental mechanics of your drone to executing complex maneuvers, we’ll break down the process into manageable segments. This guide emphasizes safe practices and responsible operation, equipping you with the knowledge to fly confidently and legally. Whether you’re aiming to capture breathtaking aerial photography or simply explore the thrill of drone flight, this comprehensive resource will serve as your ultimate companion.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding your drone’s components and associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the function of key parts and provides a glossary of common terms.
Major Drone Components
A drone comprises several interconnected systems working in harmony. Let’s examine the key components:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, hover, and maneuver. Different propeller designs optimize for speed, lift, or efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers. Brushless motors are commonly used in drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, the flight controller receives data from various sensors and uses algorithms to maintain stability and execute pilot commands. It manages motor speeds, orientation, and more.
- Battery: Provides power to the motors and other electronic components. Battery capacity and type significantly impact flight time.
- GPS Module (if equipped): Allows for autonomous flight modes, precise positioning, and return-to-home functionality.
- Camera (if equipped): Captures photos and videos. Features vary greatly depending on the drone model.
- Radio Transmitter/Receiver: Allows the pilot to control the drone wirelessly.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Here’s a quick glossary of common drone terms:
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a constant altitude.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, reducing camera shake and producing smoother footage.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): An automated function that returns the drone to its starting point.
- Throttle: Controls the drone’s vertical speed (ascending and descending).
- Yaw: Rotation of the drone around its vertical axis (turning left or right).
- Pitch: Movement of the drone’s nose up or down.
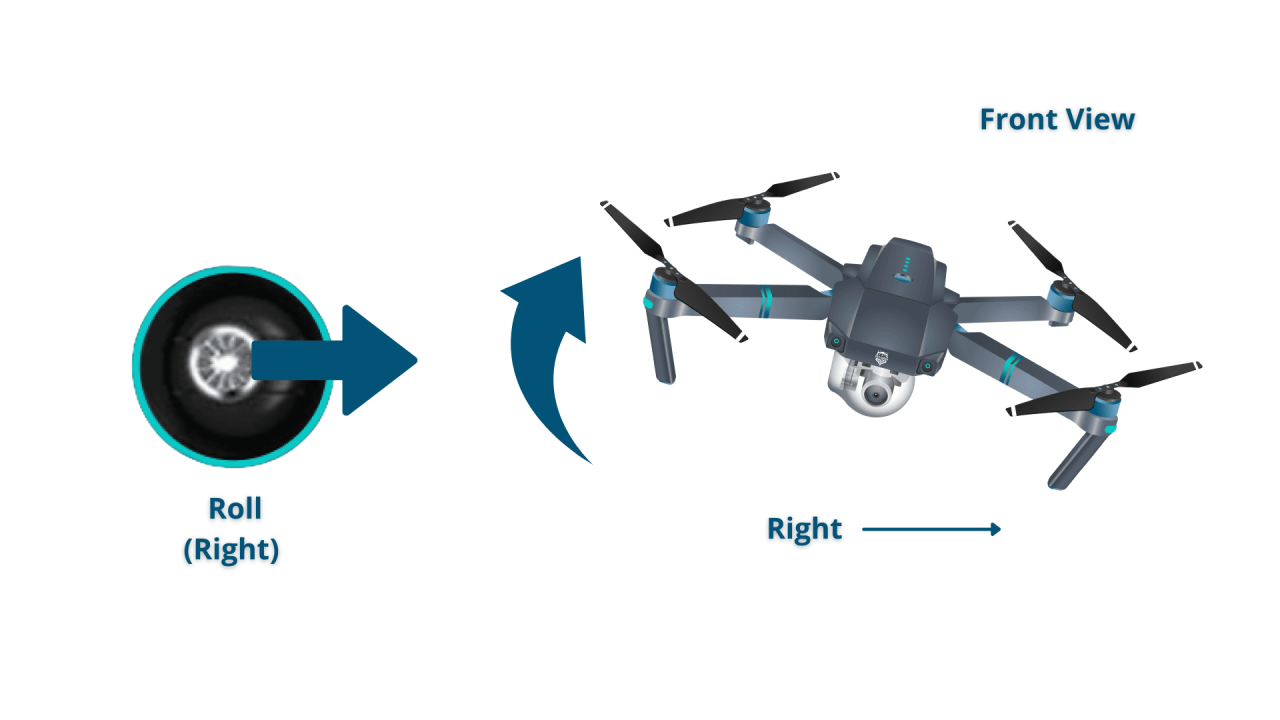
- Roll: Tilting the drone left or right.
- mAh (milliampere-hour): A measure of battery capacity.
- Flight Controller: The central processing unit of the drone.
Drone Battery Comparison
Different batteries offer varying capacities, voltages, and flight times. The choice depends on your needs and drone model.
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Voltage (V) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S 1500mAh | 1500 | 11.1 | 15-20 |
| LiPo 4S 2200mAh | 2200 | 14.8 | 25-30 |
| LiHV 3S 1800mAh | 1800 | 12.6 | 18-22 |
| LiPo 6S 5200mAh | 5200 | 22.2 | 40-50 |
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is paramount for safe drone operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously check the following:
- Battery Level: Ensure the battery is fully charged and securely connected.
- Propeller Inspection: Check for any damage or cracks in the propellers.
- Motor Function: Perform a brief motor test to verify proper operation.
- Flight Controller Calibration: Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) as needed.
- GPS Signal: Confirm a strong GPS signal before takeoff (if applicable).
- Radio Transmitter Check: Verify the transmitter is properly bound to the drone and has sufficient battery power.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess wind speed, visibility, and potential hazards.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure you are operating within legal limits and regulations.
Drone Damage Inspection
Inspect the drone for any physical damage, such as cracks, loose parts, or bent components. Pay close attention to the propellers, arms, and landing gear.
Compass and Sensor Calibration
Regular calibration of the drone’s compass and sensors is vital for accurate flight performance and stability. Consult your drone’s manual for specific calibration procedures.
Taking Off and Landing
Safe and controlled takeoffs and landings are fundamental to responsible drone operation. This section Artikels procedures for both.
Safe Takeoff Procedures
- Clear the Area: Ensure a safe, open space free from obstacles and people.
- Level Ground: Choose a level, stable surface for takeoff and landing.
- Pre-flight Checks: Complete the pre-flight checklist.
- Arm the Motors: Follow the specific arming procedure for your drone model.
- Gentle Ascent: Slowly increase throttle to initiate a controlled ascent.
- Hover: Once airborne, stabilize the drone in a hover position.
Smooth Landing Procedures

- Approach Slowly: Descend gently towards the landing area.
- Maintain Stability: Keep the drone stable and level during descent.
- Reduce Throttle Gradually: Slowly reduce throttle as the drone approaches the ground.
- Gentle Touchdown: Allow the drone to gently touch down.
- Disarm Motors: Disarm the motors after landing.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Many drones offer assisted takeoff and landing features. While convenient, understanding manual control is essential for handling unexpected situations.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is the foundation of proficient drone piloting. This section details the control sticks and common maneuvers.
Flight Control Stick Functions
Most drones utilize two control sticks:
- Left Stick: Controls pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right).
- Right Stick: Controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (vertical movement).
Basic Flight Maneuvers
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude by gently increasing throttle.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude by gently decreasing throttle.
- Turning: Rotating the drone using the right stick’s yaw control.
Common Flight Mistakes
- Sudden Movements: Avoid jerky movements of the control sticks.
- Ignoring Wind: Account for wind conditions and adjust accordingly.
- Low Battery Warning: Always heed low battery warnings and return to land promptly.
- Loss of Visual Contact: Maintain visual contact with the drone at all times.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic maneuvers, you can explore more advanced flight techniques.
Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers such as flips, rolls, and precision hovering require practice and skill. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions and safety precautions.
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the intricacies of controlling the drone itself, which you can explore further by checking out this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Proper operation ensures safe and efficient flights, ultimately leading to a rewarding drone experience.
GPS and Autonomous Flight Modes
GPS-enabled drones offer features like autonomous flight modes (e.g., waypoint navigation, follow me), greatly enhancing capabilities and ease of use.
Flying in Different Conditions
Wind, rain, and other environmental factors significantly impact drone flight. Strong winds can make control difficult, while rain can damage electronic components. Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Safe and legal drone operation is crucial. This section Artikels key safety considerations and regulations.
Safety Considerations
- Visual Line of Sight: Maintain visual contact with your drone at all times.
- Safe Distance from Obstacles: Keep a safe distance from people, buildings, and other obstacles.
- Battery Safety: Handle LiPo batteries with care; they are flammable.
- Emergency Procedures: Be prepared to handle emergencies such as loss of control or battery failure.
Local and National Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. Familiarize yourself with the specific rules and regulations in your area before flying. These often include restrictions on airspace, flight altitude, and required registration.
Responsible Drone Operation, How to operate a drone
Responsible drone operation involves respecting airspace restrictions, adhering to safety guidelines, and being considerate of others.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. This section provides guidance on optimizing image quality and composition.
Camera Settings Adjustment
Adjust camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to optimize image quality based on lighting conditions and desired effects.
Composing Compelling Shots
Use the drone’s unique perspective to create dynamic and engaging shots. Experiment with different angles, perspectives, and movements to achieve visually interesting results.
Capturing Smooth Aerial Footage
Smooth, stable footage is crucial for professional-looking videos. Use a gimbal (if equipped) and practice smooth, controlled movements to minimize camera shake.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues
Even the most reliable drones can experience malfunctions. This section provides troubleshooting steps for common problems.
Common Drone Malfunctions
Common issues include low battery warnings, motor failures, GPS signal loss, and connectivity problems.
Troubleshooting Steps
For specific troubleshooting, always consult your drone’s manual. However, general steps include checking battery levels, inspecting motors and propellers for damage, ensuring a strong GPS signal, and restarting the drone and controller.
Troubleshooting Flowchart
A flowchart would visually guide users through a systematic troubleshooting process, starting with the most common issues and branching out based on results.
Drone Maintenance and Storage: How To Operate A Drone
Proper maintenance and storage are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and its components.
Cleaning and Maintenance
Regularly clean the drone’s body, propellers, and camera lens to remove dirt and debris. Inspect for any damage and address it promptly.
Proper Storage
Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Keep the battery separate and properly stored according to its manufacturer’s instructions.
Battery Maintenance
Properly store and charge LiPo batteries to maintain their performance and extend their lifespan. Avoid overcharging or completely discharging them.
Emergency Procedures
Knowing how to handle emergencies is critical for safe drone operation. This section Artikels procedures for unexpected situations.
Handling Unexpected Situations

Loss of control, battery failure, and unexpected malfunctions require immediate action. Prioritize safe landing procedures and minimizing potential damage.
Emergency Landing
In an emergency, prioritize a safe landing. Choose a suitable landing area and execute a controlled descent, even if it means sacrificing some level of precision.
Recovering a Crashed Drone
After a crash, assess the damage and carefully recover the drone. Handle any damaged LiPo batteries with extreme caution.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a rewarding journey that combines technical skill with responsible decision-making. By understanding your drone’s components, performing thorough pre-flight checks, and practicing safe flight maneuvers, you’ll unlock a world of aerial possibilities. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and continuously hone your skills. With dedication and practice, you’ll be soaring through the skies, capturing stunning footage, and enjoying the exhilarating experience of drone flight.
Essential Questionnaire
What type of drone is best for beginners?
User-friendly drones with GPS and autonomous modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good stability and easy-to-use controls.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as taking off and landing smoothly, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide on the intricacies of flight, including advanced maneuvers and troubleshooting, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation.
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model and battery capacity. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes per charge on average.
What should I do if my drone loses connection?
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. Activate this immediately. If unavailable, attempt to regain connection; otherwise, prepare for an emergency landing.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations and procedures.
Can I fly my drone anywhere?
No. Drone flight is restricted in many areas, including airports, military bases, and national parks. Always check local regulations before flying.
